×
- Live Chat
- 1-888-511-3595

My Garage
My Account
Cart
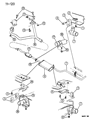
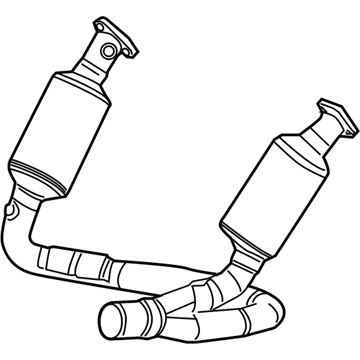
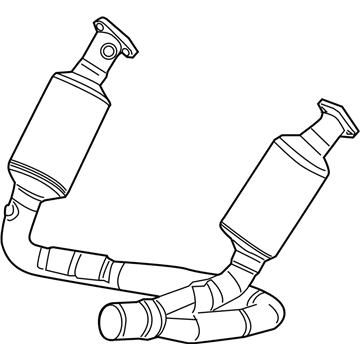
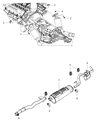
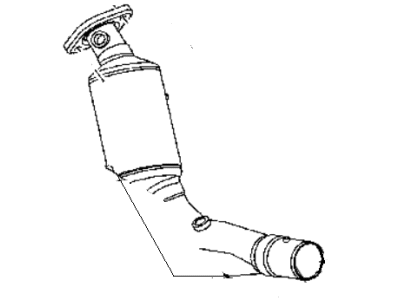
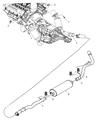
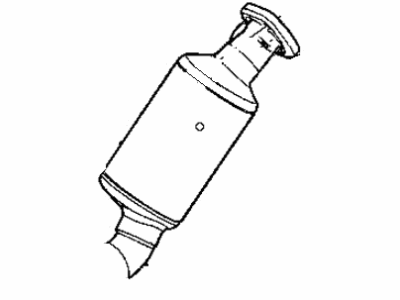
Genuine Dodge Dakota Catalytic Converter
Cat. Converter- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
44 Catalytic Converters found
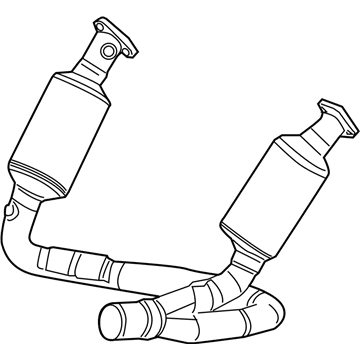
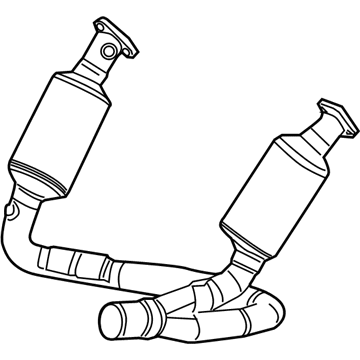
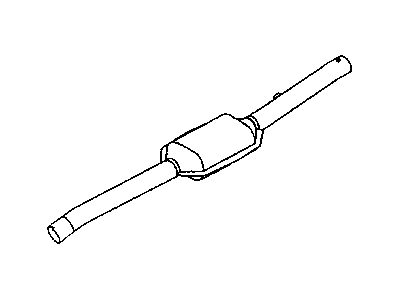
Dodge Dakota Converter-Exhaust
Part Number: 52855898AD$3019.50 MSRP: $4430.00You Save: $1410.50 (32%)Dodge Dakota Converter-Exhaust
Part Number: 52855898AC$3019.50 MSRP: $4430.00You Save: $1410.50 (32%)
| Page 1 of 3 |Next >
1-20 of 44 Results
Dodge Dakota Catalytic Converter
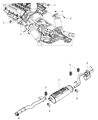
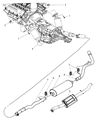
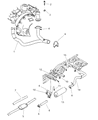
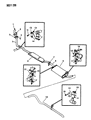
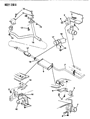
The Dodge Dakota Catalytic Converter is a very vital part of the automobile emission system which burns the undesirable gases such as CO, HC, NOx into less hazardous products like water, CO2 and nitrogen. The function of this part involves using catalyst materials such as platinum, palladium, and rhodium as it developed a honeycomb structure it achieves oxidation and reduction reactions to cut emissions. There are also different Categories of Catalytic Converters available for Dakota vehicles for instance direct fit and universal converters whereby, the universal converters will need to be cut and then clamped on but the direct fit converters can easily replace the factory converters. The care and proper replacement of the damaged parts on the Dodge Dakota Catalytic Converter are critical to getting the premier performance and fuel consumption.
Looking for affordable and high-quality auto parts? Then you have already arrived at the proper online shop. We offer all Dodge Dakota Catalytic Converter at great affordable prices. Moreover, all genuine Dodge Dakota Catalytic Converter come with a manufacturer's warranty. In the long run, you would realize you have saved a lot of trouble and money with OEM parts from here.
Dodge Dakota Catalytic Converter Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: How Can I Check and Replace a Malfunctioning Catalytic Converter on Dodge Dakota?A: A catalytic converter (or catalyst) is an emission control device that reduces certain pollutants in the exhaust gas stream, with two types available, an oxidation catalyst reducing hydrocarbons (HC) and carbon monoxide (CO), and a reduction catalyst reducing oxides of nitrogen (NOx). To check a malfunctioning converter, expensive test equipment is needed, so it's best to consult a dealer or authorized emission inspection facility for diagnosis and repair. During underbody servicing, inspect the converter for leaks, corrosion, dents, and other damage, and replace it if necessary. To check for a restricted converter, use a vacuum gauge to diagnose the effect of a blocked exhaust on intake vacuum. If the exhaust system is restricted, it might indicate a plugged catalytic converter or a restricted exhaust pipe or muffler. For replacement, spray penetrant on exhaust pipe-to-exhaust manifold bolts and clamp bolts to loosen them up. Disconnect and remove Oxygen Sensors. Unscrew upper exhaust pipe-to-exhaust manifold flange bolts and loosen the clamp securing the slip joint between the two sides of the crossover pipe. If replacing the right catalytic converter, also loosen the clamp securing the slip joint between the right exhaust pipe and the premuffler. Remove the catalytic converter assembly, discard the old flange gasket, and install a new one during reinstallation using new bolts and clamps as recommended by Dodge. Coat threads with anti-seize compound for ease of future removal and tighten all fasteners securely.
Related Dodge Dakota Parts
Browse by Year
2011 Catalytic Converter 2010 Catalytic Converter 2009 Catalytic Converter 2008 Catalytic Converter 2007 Catalytic Converter 2006 Catalytic Converter 2005 Catalytic Converter 2004 Catalytic Converter 2003 Catalytic Converter 2002 Catalytic Converter 2001 Catalytic Converter 2000 Catalytic Converter 1999 Catalytic Converter 1998 Catalytic Converter 1997 Catalytic Converter 1996 Catalytic Converter 1995 Catalytic Converter 1994 Catalytic Converter 1993 Catalytic Converter 1992 Catalytic Converter 1991 Catalytic Converter 1990 Catalytic Converter 1989 Catalytic Converter 1988 Catalytic Converter 1987 Catalytic Converter