×
- Live Chat
- 1-888-511-3595

My Garage
My Account
Cart
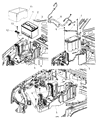
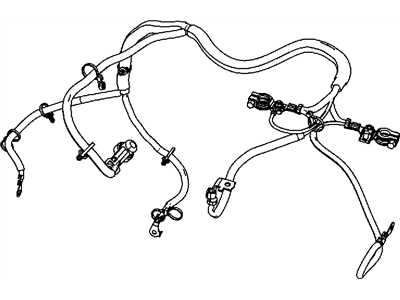
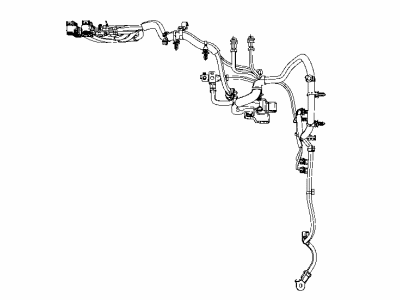
Genuine Jeep Wrangler Battery Cable
Car Battery Cable- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
59 Battery Cables found
Jeep Wrangler CABLE-BATTERY CHARGER
Part Number: 5190308AA$699.23 MSRP: $1080.00You Save: $380.77 (36%)Jeep Wrangler CABLE-BATTERY CHARGER
Part Number: 5185053AC$310.20 MSRP: $449.00You Save: $138.80 (31%)Jeep Wrangler CABLE-BATTERY CHARGER
Part Number: 5185051AC$384.10 MSRP: $587.00You Save: $202.90 (35%)Jeep Wrangler CABLE-BATTERY CHARGER
Part Number: 5190284AB$384.10 MSRP: $587.00You Save: $202.90 (35%)Jeep Wrangler Cable-Battery Charger
Part Number: 5190287AB$403.74 MSRP: $617.00You Save: $213.26 (35%)Jeep Wrangler Cable-Battery Charger
Part Number: 5190286AB$409.20 MSRP: $625.00You Save: $215.80 (35%)Jeep Wrangler CABLE-BATTERY CHARGER
Part Number: 5185055AC$488.86 MSRP: $750.00You Save: $261.14 (35%)Jeep Wrangler CABLE-BATTERY CHARGER
Part Number: 5190285AC$475.76 MSRP: $730.00You Save: $254.24 (35%)
| Page 1 of 3 |Next >
1-20 of 59 Results
Jeep Wrangler Battery Cable
Battery Cable in Jeep Wrangler vehicles refer to electrical wires that provide a pathway through which electrical current from the battery to other electrical equipments so as to form the starter and ignite the engine. These cables includes a power supply cable commonly known as the 'comma' cable and an earth cable that acts as the electrical ground which makes up an essential loop in a car's power system. By the years, various types of the Battery Cable may have been used in several models of the Jeep Wrangler though particular models are not highlighted. The first area where battery relay corrects attention is their status; old or worn cables are likely to cause starting troubles; therefore, it is crucial to maintain these parts to achieve excellent car performance. Good battery cables are likely to facilitate proper functioning of the Jeep Wrangler irrespective of the kind of engine and the transmission system.
Looking for affordable and high-quality auto parts? Then you have already arrived at the proper online shop. We offer all Jeep Wrangler Battery Cable at great affordable prices. Moreover, all genuine Jeep Wrangler Battery Cable come with a manufacturer's warranty. In the long run, you would realize you have saved a lot of trouble and money with OEM parts from here.
Jeep Wrangler Battery Cable Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: How to inspect and replace battery cables on Jeep Wrangler?A: Inspect the entire length of each battery cable periodically for damage, cracked or burned insulation and corrosion as poor battery connections can cause starting problems and decreased engine performance. Check the cable-to-terminal connections at the ends of the cables for cracks, loose wire strands and corrosion. White, fluffy deposits under the insulation at the cable terminal connection indicate corrosion and the need for replacement. Also, check the terminals for distortion, missing mounting bolts and corrosion. When removing the cables, always disconnect the negative cable first and hook it up last to avoid shorting the battery. Disconnect the old cables from the battery, then trace each of them to their opposite ends and detach them from the Starter Solenoid and ground terminals. Note the routing of each cable for correct installation. If replacing the cables, take the old ones with you when buying new ones to ensure you get identical parts. Positive cables are usually red, larger in cross section and have a larger diameter battery post clamp, while ground cables are usually black, smaller in cross-section and have a slightly smaller diameter clamp for the negative post. Clean the threads of the solenoid or ground connection with a wire brush to remove rust and corrosion. Apply a light coat of battery terminal corrosion inhibitor, or petroleum jelly, to the threads to prevent future corrosion. Attach the cable to the solenoid or ground connection and tighten the mounting nut/bolt securely. Before connecting a new cable to the battery, ensure that it reaches the battery post without having to be stretched. Connect the positive cable first, followed by the negative cable.
Related Jeep Wrangler Parts
Browse by Year
2024 Battery Cable 2023 Battery Cable 2022 Battery Cable 2020 Battery Cable 2019 Battery Cable 2018 Battery Cable 2011 Battery Cable 2010 Battery Cable 2009 Battery Cable 2008 Battery Cable 2007 Battery Cable 2006 Battery Cable 2005 Battery Cable 2004 Battery Cable 2003 Battery Cable 2002 Battery Cable 2001 Battery Cable 2000 Battery Cable 1997 Battery Cable 1995 Battery Cable 1994 Battery Cable 1993 Battery Cable 1992 Battery Cable 1991 Battery Cable